 PDF(1731 KB)
PDF(1731 KB)


 PDF(1731 KB)
PDF(1731 KB)
 PDF(1731 KB)
PDF(1731 KB)
旅游者饮食涉入对行为意向的影响路径
INFLUENCING PATHS OF TOURIST FOOD INVOLVEMENT ON BEHAVIORAL INTENTION
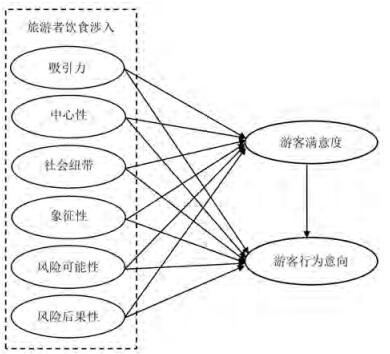
旅游情境下的饮食消费成为社会关注的热点和国外旅游研究的重点领域。旅游者饮食涉入是游客在饮食决策和活动中所展现的一种心理状态及其投入程度,是探讨旅游者饮食消费心理和行为的重要视角。在借鉴国内外研究的基础上,结合线下和线上调研数据,构建并解读旅游者饮食涉入的结构特征及其对行为意向的影响路径。结果表明,旅游者饮食涉入包括吸引力、中心性、社会纽带、象征性、风险可能性和风险后果性6个维度,并对消费满意度和行为意向有显著影响,但不同维度影响存在差异。旅游者饮食涉入内容结构与影响路径呈现出饮食消费心理的复杂性与价值取向的转型,旅游者对饮食的认知及其赋予价值影响涉入程度,并受到旅游地饮食消费情境的调节。旅游者饮食涉入研究为理解旅游者饮食消费行为和目的地美食营销提供参考。
In the context of tourism, food consumption has become a prominent topic of social concern and a key focus in international tourism research. However, compared with traditional food culture and contemporary food practice, the breadth and depth of food tourism research in China urgently need to be strengthened. Tourists' food involvement reflects their psychological state and level of engagement in food-related decisions and activities, offering a crucial perspective for studying tourists' food consumption behavior. Drawing on domestic and international research, this article integrates offline and online survey data to construct and interpret the structural characteristics of tourists' food involvement, as well as its impact pathways on behavioral intentions. The results indicate that tourists' food involvement consists of six dimensions: attractiveness, centrality, social bonds, symbolism, risk possibility, and risk consequences. These dimensions significantly influence consumer satisfaction and behavioral intentions, although their impacts vary across dimensions. The structural content and impact pathways of tourists' food involvement highlight the complexity of food consumption psychology and the evolving nature of value orientation. Tourists' perceptions of food and the values they attribute to it influence their level of involvement, which is moderated by the food consumption context at tourist destinations.
food involvement / tourist food consumption / behavioral intention / influence paths
| 1 |
余凤龙, 徐羽可, 侯兵, 等. 因何而食: 旅游者饮食动机及其影响因素研究[J]. 旅游科学, 2024, 38 (1): 38- 56.
|
| 2 |
程励, 陆佑海, 李登黎, 等. 儒家文化视域下美食旅游目的地品牌个性及影响[J]. 旅游学刊, 2018, 33 (1): 25- 41.
|
| 3 |
戴斌. 美食新动能, 旅游高品质: 2023年中国美食旅游发展报告[EB/OL]. (2023-09-18)[2024-08-03]. https://www.ctaweb.org.cn/index.php?m=home&c=View&a=index&aid=5323&lang=cn.
Dai Bin. New driving force of cuisine, high-quality tourism: China food tourism development report(2023)[EB/OL]. (2023-09-18)[2024-08-03]. https://www.ctaweb.org.cn/index.php?m=home&c=View&a=index&aid=5323&lang=cn.
|
| 4 |
张光直. 中国文化中的饮食[M]. 桂林: 广西师范大学出版社, 2023: 1- 10.
|
| 5 |
余凤龙, 徐留倩, 陈悦. 旅游者地方饮食文化认同的构建机制: 以长沙文和友为例[J]. 美食研究, 2024, 41 (1): 18- 26.
|
| 6 |
谢涤湘, 谢晓亮, 兰妍, 等. 老年人的休闲涉入与地方依恋: 基于广州城市公园的实证研究[J]. 地理科学, 2022, 42 (4): 692- 701.
|
| 7 |
|
| 8 |
|
| 9 |
|
| 10 |
|
| 11 |
|
| 12 |
|
| 13 |
|
| 14 |
余凤龙, 潘薇, 徐羽可. 旅游者饮食舒适度构成要素及影响机制研究[J]. 人文地理, 2021, 36 (4): 185- 192.
|
| 15 |
|
| 16 |
|
| 17 |
|
| 18 |
|
| 19 |
周瑜, 侯平平. 饮食相关人格特质的前因、结果与作用机制研究: 一个文献综述[J]. 旅游论坛, 2022, 15 (6): 95- 106.
|
| 20 |
|
| 21 |
|
| 22 |
林德荣, 郭璇瑄. 服务接触对游客美食消费意向的影响机制研究[J]. 吉林大学社会科学学报, 2020, 60 (3): 226- 234.
|
| 23 |
徐羽可, 余凤龙, 潘薇. 美食旅游研究进展与启示[J]. 美食研究, 2021, 38 (1): 24- 32.
|
| 24 |
|
| 25 |
张宏梅, 陆林. 游客涉入及其与旅游动机和游客满意度的结构关系: 以桂林、阳朔入境旅游者为例[J]. 预测, 2010, 29 (2): 64- 69.
|
| 26 |
|
| 27 |
|
| 28 |
|
| 29 |
陆相林, 孙中伟. 旅游涉入、满意度、地方依恋作用机制研究: 以西柏坡红色游客为例[J]. 干旱区资源与环境, 2017, 31 (7): 183- 188.
|
| 30 |
|
| 31 |
|
| 32 |
|
| 33 |
|
| 34 |
王婷, 薛涛, 王芳, 等. 基于抗疫音乐视频共情的目的地涉入对行为意图的影响研究[J]. 西南大学学报(自然科学版), 2020, 42 (9): 26- 39.
|
| 35 |
|
| 36 |
|
| 37 |
|
| 38 |
周玲强, 林青青. 基于维度层次的背包游客动机与涉入的关系研究[J]. 浙江大学学报(人文社会科学版), 2013, 43 (3): 155- 163.
|
| 39 |
蔡礼彬, 程晓盈. 情感认知评价视角下文化遗产城市游客遗产责任行为形成机制[J]. 自然资源学报, 2024, 39 (6): 1278- 1298.
|
| 40 |
王华, 李兰. 生态旅游涉入、群体规范对旅游者环境友好行为意愿的影响: 以观鸟旅游者为例[J]. 旅游科学, 2018, 32 (1): 86- 95.
|
| 41 |
弗里德曼. 食物: 味道的历史[M]. 董舒琪, 译. 杭州: 浙江大学出版社, 2015: 55-75.
Friedman. Food: The History of Taste[M]. Dong Shuqi, trans. Hangzhou: Zhejiang University Press, 2015: 55-75.
|
| 42 |
刘彬, 阚兴龙, 陈忠暖. 支持性体验与高峰体验: 旅游者饮食消费研究——以成都为例[J]. 人文地理, 2017, 32 (2): 23- 29.
|
| 43 |
|
| 44 |
曾国军, 李忠奇, 王龙杰, 等. 流动群体饮食实践中的伦理变迁与身份协商: 基于主体性、社会性、地方性的分析[J]. 人文地理, 2013, 38 (6): 23- 33.
|
/
| 〈 |
|
〉 |