 PDF(1966 KB)
PDF(1966 KB)


 PDF(1966 KB)
PDF(1966 KB)
 PDF(1966 KB)
PDF(1966 KB)
面向中国式现代化的经济增长新动能:技术、数据与关系
NEW DYNAMICS OF ECONOMIC GROWTH TOWARD CHINESE MODERNIZATION: TECHNOLOGY, DATA AND RELATIONSHIPS
探讨中国式现代化进程中经济增长新动能是经济地理学面临的时代之责。本文从理论层面上阐释了技术、数据、关系新型三要素对经济增长的驱动机理,并采用地理探测器实证了新型三要素取代传统三要素的变革趋势。研究发现:①新型三要素凭借其增量性和无限性的优势能够为经济增长持续供能,将逐步取代土地、劳动力、资本传统三要素的核心地位,成为新时代中国经济增长的新动力。②关系要素能够促进区域资源的互动和重组,加速资源有效配置和财富积累,激活区域发展动力。③新旧三要素的经济驱动效应呈现显著的城市异质性。新型三要素已成为大城市经济增长的核心动能,传统三要素的驱动作用明显降低;对于中小城市而言传统三要素仍是经济增长的核心驱动力。
Exploring new drivers of economic growth in the process of Chinese modernization is a responsibility that economic geography faces in this era. This paper theoretically elucidates how the new triad of technology, data, and relationship drives economic growth. By employing geographical detectors, we empirically demonstrate the transformative trend where these new elements are replacing the traditional triplet. The study reveals several key findings: 1) With their advantages of incrementality, cumulativeness, and infinity, the new triplet can continuously fuel economic growth. They are gradually supplanting the core position held by the traditional triplet of land, labor, and capital in the economic growth driving force system, emerging as the new impetus for China's economic growth in the new era. 2) As a hidden and incremental factor, relationship resources play a crucial driving role in regional economic growth. They facilitate the interaction and reorganization of regional resources, providing convenient connection channels for the flow of other resource elements. 3) The economic driving effects of the new and old triplets exhibit significant spatial heterogeneity.
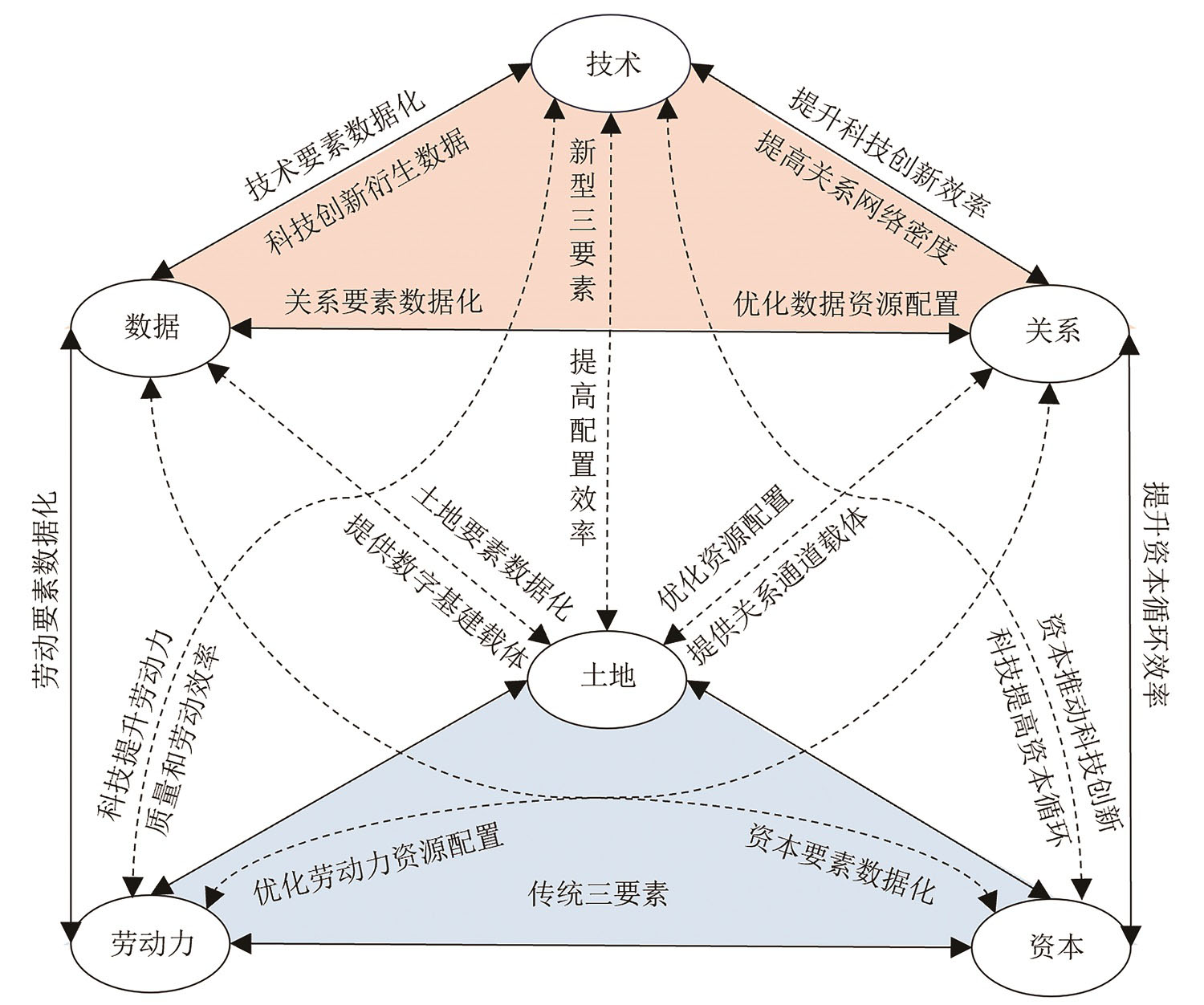
regional economic growth / traditional three factors / new three factors
| 1 |
曾刚, 胡森林. 百年未有之大变局下中国区域发展格局演变[J]. 经济地理, 2021, 41(10): 42-48, 69.
|
| 2 |
陈梦根, 侯园园. 中国经济增长动力结构变迁: 2000—2019[J]. 经济研究, 2024, 59(1): 53- 71.
|
| 3 |
|
| 4 |
乔文怡, 仲天泽, 黄贤金. 1990年以来中国国土空间规划研究的特征和进展[J]. 人文地理, 2024, 39(5): 1-12, 95.
|
| 5 |
|
| 6 |
严成樑. 现代经济增长理论的发展脉络与未来展望——兼从中国经济增长看现代经济增长理论的缺陷[J]. 经济研究, 2020, 55(7): 191- 208.
|
| 7 |
于立, 王建林. 生产要素理论新论——兼论数据要素的共性和特性[J]. 经济与管理研究, 2020, 41(4): 62- 73.
|
| 8 |
|
| 9 |
许宪春, 张钟文, 胡亚茹. 数据资产统计与核算问题研究[J]. 管理世界, 2022, 38(2): 16-30, 2.
|
| 10 |
徐翔, 厉克奥博, 田晓轩. 数据生产要素研究进展[J]. 经济学动态, 2021(4): 142- 158.
|
| 11 |
谢康, 夏正豪, 肖静华. 大数据成为现实生产要素的企业实现机制: 产品创新视角[J]. 中国工业经济, 2020(5): 42- 60.
|
| 12 |
孙久文, 周孝伦. 黄河流域地区与长江经济带高质量发展的动能转换与策略重点比较[J]. 资源科学, 2024, 46(3): 435- 449.
|
| 13 |
郑江淮, 宋建, 张玉昌, 等. 中国经济增长新旧动能转换的进展评估[J]. 中国工业经济, 2018(6): 24- 42.
|
| 14 |
苗长虹. 变革中的西方经济地理学: 制度、文化、关系与尺度转向[J]. 人文地理, 2004, 19(4): 68- 76.
|
| 15 |
|
| 16 |
李小建, 罗庆. 经济地理学的关系转向评述[J]. 世界地理研究, 2007, 16(4): 19- 27.
|
| 17 |
|
| 18 |
|
| 19 |
|
| 20 |
方福前. 寻找供给侧结构性改革的理论源头[J]. 中国社会科学, 2017(7): 49-69, 205.
|
| 21 |
|
| 22 |
张来明, 李建伟. 收入分配与经济增长的理论关系和实证分析[J]. 管理世界, 2016, 32(11): 1- 10.
|
| 23 |
杨凤林, 陈金贤, 杨晶玉. 经济增长理论及其发展[J]. 经济科学, 1996(1): 71- 75.
|
| 24 |
樊纲, 易纲, 李岩. 关于中国经济增长与全要素生产率的理论思考[J]. 经济研究, 2003(8): 13-20, 90.
|
| 25 |
|
| 26 |
潘士远, 史晋川. 内生经济增长理论: 一个文献综述[J]. 经济学(季刊), 2002, 1(4): 753- 786.
|
| 27 |
|
| 28 |
曾鹏, 朱柳慧. 关系视角下乡村空间认知与转型路径研究[J]. 人文地理, 2022, 37(1): 1-8, 17.
|
| 29 |
|
| 30 |
|
| 31 |
|
| 32 |
|
| 33 |
马海涛, 胡夏青. 城市网络视角下的中国科技创新功能区划研究[J]. 地理学报, 2022, 77(12): 3104- 3124.
|
| 34 |
尚勇敏, 曾刚. 科技创新推动区域经济发展模式转型: 作用和机制[J]. 地理研究, 2017, 36(12): 2279- 2290.
|
| 35 |
武宵旭, 任保平, 葛鹏飞. 黄河流域技术创新与绿色发展的耦合协调关系[J]. 中国人口·资源与环境, 2022, 32(8): 20- 28.
|
| 36 |
蔡继明, 刘媛, 高宏, 等. 数据要素参与价值创造的途径——基于广义价值论的一般均衡分析[J]. 管理世界, 2022, 38(7): 108- 121.
|
| 37 |
杨俊, 李小明, 黄守军. 大数据、技术进步与经济增长——大数据作为生产要素的一个内生增长理论[J]. 经济研究, 2022, 57(4): 103- 119.
|
| 38 |
娄帆, 李小建, 白燕飞. 1978年以来中国沿海与内陆经济格局的转折分析[J]. 中国人口·资源与环境, 2021, 31(5): 1- 11.
|
| 39 |
孙久文, 蒋治, 胡俊彦. 新时代中国城市高质量发展的时空演进格局与驱动因素[J]. 地理研究, 2022, 41(7): 1864- 1882.
|
| 40 |
王嘉炜, 曾刚, 朱妮娜, 等. 市场整合、对外开放与长三角区域高质量发展[J]. 经济地理, 2023, 43(11): 8- 16.
|
| 41 |
范庆泉, 储成君, 高佳宁. 环境规制、产业结构升级对经济高质量发展的影响[J]. 中国人口·资源与环境, 2020, 30(6): 84- 94.
|
| 42 |
刘瑞明, 毛宇, 亢延锟. 制度松绑、市场活力激发与旅游经济发展——来自中国文化体制改革的证据[J]. 经济研究, 2020, 55(1): 115- 131.
|
| 43 |
张治栋, 廖常文. 全要素生产率与经济高质量发展——基于政府干预视角[J]. 软科学, 2019, 33(12): 29- 35.
|
| 44 |
李江苏, 孟琳琳, 李韦华, 等. 黄河流域生产性服务业综合发展水平时空演变及影响因素分析[J]. 人文地理, 2023, 38(2): 116- 125.
|
| 45 |
何田, 廖和平, 孙平军, 等. 西南喀斯特区贫困劳动力转移就业空间格局及影响因素——以云南省永善县为例[J]. 人文地理, 2022, 37(4): 158-165, 181.
|
| 46 |
|
| 47 |
杨新铭. 党探索社会主义市场经济体制的历程、经验及支撑性制度建设[J]. 经济学动态, 2021(6): 16- 30.
|
| 48 |
蒋自然, 樊俊杰, 黎晨晟, 等. 数字经济发展对中国制造业生产效率的影响: 空间效应与传导机制[J]. 人文地理, 2024, 39(3): 72-80, 122.
|
| 49 |
刘涛雄, 张亚迪, 戎珂, 等. 数据要素成为中国经济增长新动能的机制探析[J]. 经济研究, 2024, 59(10): 19- 36.
|
| 50 |
林攀, 余斌, 刘杨洋, 等. 中国新旧动能转换的空间分异及影响因素研究[J]. 经济地理, 2021, 41(11): 19- 27.
|
/
| 〈 |
|
〉 |