 PDF(1833 KB)
PDF(1833 KB)


 PDF(1833 KB)
PDF(1833 KB)
 PDF(1833 KB)
PDF(1833 KB)
黄河滩区生态移民生计能力对主观福祉影响的组态路径分析
A CONFIGURATION PATH ANALYSIS OF THE IMPACT OF ECOLOGICAL MIGRANTS' LIVELIHOOD ABILITY ON SUBJECTIVE WELL-BEING IN THE YELLOW RIVER BEACH AREA
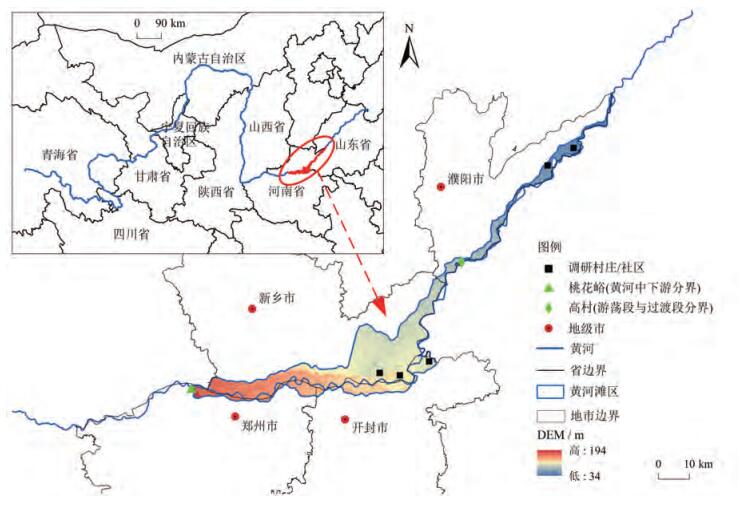
探讨生计能力对黄河滩区生态移民主观福祉的影响,对于巩固移民成效、增进移民福祉具有重要实践意义。本文以生态搬迁基本完成的黄河滩区(河南段)为例,分析移民前后生计能力和主观福祉的变化,利用模糊集定性比较揭示不同生计能力组态路径对主观福祉的影响及其变化。结果表明:①黄河滩区移民后居民主观福祉呈上升趋势。②单一维度生计能力在移民前后均不能成为提升移民主观福祉的必要条件,但仍对其产生重要影响,尤其以心理调试能力和环境适应能力最为关键。③生态移民前后组态对比,经济维稳能力对主观福祉的影响及其重要性增强,社会交往能力和环境适应能力对主观福祉的影响及其重要性相对减弱,基本劳动能力和心理调试能力对主观福祉的影响及其重要性无变化。据此,本文提出了提升黄河滩区移民主观福祉的针对性建议。
To explore the impact of livelihood ability on the subjective well-being of ecological migrants in the Yellow River Beach Area is of great practical significance for consolidating the effect of migration and improving the well-being of migrants. Taking the Yellow River Beach Area (Henan section) as an example, this paper analyzes the changes of livelihood ability and subjective well-being before and after migration, and uses fuzzy set qualitative comparison to reveal the influence and changes of different configuration path of livelihood ability indicators on subjective well-being. The results show that: 1) The subjective well-being of the residents in the Yellow River Beach Area is on the rise. 2) A single dimension of livelihood ability cannot be a necessary condition for improving the subjective well-being of migrants before and after migration, but it still has an important impact on the it, especially the psychological adjustment ability and environmental adaptation ability. 3) The influence and importance of economic stability maintenance ability on subjective well-being are enhanced, the influence and importance of social communication ability and environmental adaptation ability on subjective well-being are relatively weakened. Therefore, this paper puts forward some suggestions to improve the subjective well-being of immigrants.
主观福祉 / 生计能力 / 生态移民 / 模糊集定性比较 / 黄河滩区
subjective well-being / livelihood ability / ecological migration / qualitative comparison of fuzzy sets / Yellow River beach area
| 1 |
徐文文. 增进民生福祉的发展诉求: 内涵、根源及意义[J]. 经济问题, 2023(12): 10- 15.
|
| 2 |
李聪, 刘杰, 黎洁. 陕西易地扶贫搬迁综合效应评估及政策创新[J]. 西安交通大学学报(社会科学版), 2023, 43(6): 95- 105.
|
| 3 |
胡西武, 刘小鹏, 黄越, 等. 宁夏生态移民村空间剥夺测度及影响因素[J]. 地理学报, 2020, 75(10): 2224- 2240.
|
| 4 |
张娜, 完德吉. 生态移民社区教育实践与可持续发展——基于三江源生态移民社区的田野考察[J]. 民族教育研究, 2023, 34(5): 125- 133.
|
| 5 |
王帅, 范蒙, 邬友, 等. 地方性感知、地方认同与好客行为——以内蒙古敖鲁古雅乡生态移民为例[J]. 干旱区资源与环境, 2024, 38(9): 199- 208.
|
| 6 |
张梦尧. 三江源地区生态移民生计转型与心理适应——以青海智格日村为个案[J]. 北方民族大学学报, 2022(5): 83- 92.
|
| 7 |
王娅, 刘洋, 周立华. 祁连山北麓生态移民的生计风险与应对策略选择——以武威市为例[J]. 自然资源学报, 2022, 37(2): 521- 537.
|
| 8 |
徐如明. 民族地区生态移民生计资本对其社会融入的影响研究——基于宁夏银川市生态移民区的实证调查[J]. 民族学论丛, 2024(2): 101- 110.
|
| 9 |
赵坤, 杜澍, 沈迟. 自然保护地管控对原住居民民生与生态移民意愿影响[J]. 城市发展研究, 2021, 28(9): 50-57, 65.
|
| 10 |
陈胜东, 周丙娟. 生态移民政策实施农户满意度及其影响因素分析——以赣南原中央苏区为例[J]. 农林经济管理学报, 2020, 19(5): 602- 610.
|
| 11 |
王亚娟, 孔福星, 刘小鹏, 等. 中国生态移民村社会空间的生产分析——以宁夏固原市典型生态移民村为例[J]. 经济地理, 2020, 40(11): 158- 166.
|
| 12 |
魏旭红, 赵雪雁. 易地扶贫搬迁对山区农户福祉的影响——以陇南山区为例[J]. 自然资源学报, 2024, 39(5): 1068- 1083.
|
| 13 |
邰秀军, 芦利广, 杨鑫, 等. 沙化区生态移民的沙化感知、社会影响和适应性策略[J]. 中国人口·资源与环境, 2020, 30(3): 168- 176.
|
| 14 |
李静, 王月金. 健康与农民主观福祉的关系分析——基于全国5省(区)1000个农户的调查[J]. 中国农村经济, 2015(10): 80- 88.
|
| 15 |
袁东波, 陈美球, 廖彩荣, 等. 土地转出农户主观福祉现状及其影响因素分析——基于生计资本视角[J]. 中国土地科学, 2019, 33(3): 25- 33.
|
| 16 |
黄甘霖, 姜亚琼, 刘志锋, 等. 人类福祉研究进展——基于可持续科学视角[J]. 生态学报, 2016, 36(23): 7519- 7527.
|
| 17 |
刘迪, 陈海, 张杰, 等. 黄土丘陵沟壑区村域客观福祉评估及其对农民主观福祉的影响——以陕西省米脂县为例[J]. 地理科学, 2023, 43(3): 530- 540.
|
| 18 |
|
| 19 |
|
| 20 |
|
| 21 |
徐荣林, 吴昱芳, 石金莲. 基于旅游感知视角的居民主观福祉影响因素研究——以九寨沟国家级自然保护区为例[J]. 南京工业大学学报(社会科学版), 2017, 16(4): 104- 114.
|
| 22 |
岳丽莹, 李开明, 吴瑞君. 城市人均受教育水平对居民主观幸福感的影响: 基于多尺度模型的研究[J]. 人文地理, 2021, 36(6): 53- 59.
|
| 23 |
|
| 24 |
陈文婷, 陈海, 刘迪, 等. 社区环境对农村居民主观福祉的影响——基于陕西省洛川县的实证[J]. 人文地理, 2023, 38(5): 36-43, 171.
|
| 25 |
李雪萍, 魏爱春. 摆动型生计: 生计能力视域下的生存策略选择——以重庆市M镇易地扶贫搬迁安置点为例[J]. 吉首大学学报(社会科学版), 2020, 41(4): 65- 74.
|
| 26 |
杨红娟, 黄友弛. 农户易地扶贫搬迁后生计能力提升的内外动力作用研究[J]. 经济问题探索, 2023(10): 98- 114.
|
| 27 |
李惠梅, 张雄, 张俊峰, 等. 自然资源保护对参与者多维福祉的影响——以黄河源头玛多牧民为例[J]. 生态学报, 2014, 34(22): 6767- 6777.
|
| 28 |
刘燕, 魏勃. 可行能力理论视角下脱贫农户发展能力的提升路径探究[J]. 农业经济, 2023(6): 98- 100.
|
| 29 |
王振振, 王立剑. 精准扶贫可以提升农村贫困户可持续生计吗?——基于陕西省70个县(区)的调查[J]. 农业经济问题, 2019(4): 71- 87.
|
| 30 |
苏芳. 乡村振兴背景下农户旅游生计转型对生计能力的影响研究[J]. 贵州社会科学, 2023(2): 144- 153.
|
| 31 |
阿玛蒂亚·森. 以自由看待发展[M]. 北京: 中国人民大学出版社, 2002: 62- 64.
|
| 32 |
韩喜平, 刘永梅. 中国现代民生福祉增进轨迹——基于民生制度与民生能力建设的视角[J]. 社会科学辑刊, 2018(3): 138- 143.
|
| 33 |
周晓春, 方舒, 黄进. 金融福祉: 促进青年发展的新工具[J]. 中国青年社会科学, 2021, 40(4): 83- 90.
|
| 34 |
李倩娜, 姚娟, 付鹏飞. 世界自然遗产地生态移民生计能力与适应策略——基于适应水平的中介作用[J]. 地域研究与开发, 2024, 43(1): 140- 145.
|
| 35 |
宁德鹏, 何玲玲. 从脱贫攻坚到共同富裕: 易地扶贫搬迁后续治理模式创新研究[J]. 中国行政管理, 2024, 40(8): 109- 117.
|
| 36 |
殷宇超, 蔡银莺. 城中村拆迁还建居民家庭住房租赁与生计能力提升——以武汉市汉阳区八个拆迁安置小区为例[J]. 城市问题, 2020(9): 86-93, 103.
|
| 37 |
王晓刚, 陈红, 叶家璨. 从安身到安心: 民族地区扶贫安置社区社会心理服务探索——基于凉山州昭觉县的实地调查[J]. 首都师范大学学报(社会科学版), 2024(5): 172- 180.
|
| 38 |
刘伟, 黎洁. 提升或损伤?易地扶贫搬迁对农户生计能力的影响[J]. 中国农业大学学报, 2019, 24(3): 210- 218.
|
| 39 |
贺艳华, 刘聪, 周国华, 等. 长江经济带城乡居民福祉测度及其差异[J]. 热带地理, 2021, 41(2): 327- 339.
|
| 40 |
陈宏胜, 王兴平, 刘晔, 等. 城镇化与居民主观福祉关系研究——兼论对城乡规划的检视与启示[J]. 城市规划, 2020, 44(7): 18-27, 90.
|
| 41 |
杜运周, 贾良定. 组态视角与定性比较分析(QCA): 管理学研究的一条新道路[J]. 管理世界, 2017(6): 155- 167.
|
| 42 |
张明, 杜运周. 组织与管理研究中QCA方法的应用: 定位、策略和方向[J]. 管理学报, 2019, 16(9): 1312- 1323.
|
/
| 〈 |
|
〉 |