 PDF(1711 KB)
PDF(1711 KB)


 PDF(1711 KB)
PDF(1711 KB)
 PDF(1711 KB)
PDF(1711 KB)
中国省域土地资源错配对其城乡融合发展的影响
THE IMPACT OF MISMATCHED LAND RESOURCES IN CHINESE PROVINCES ON THEIR URBAN-RURAL INTEGRATION DEVELOPMENT
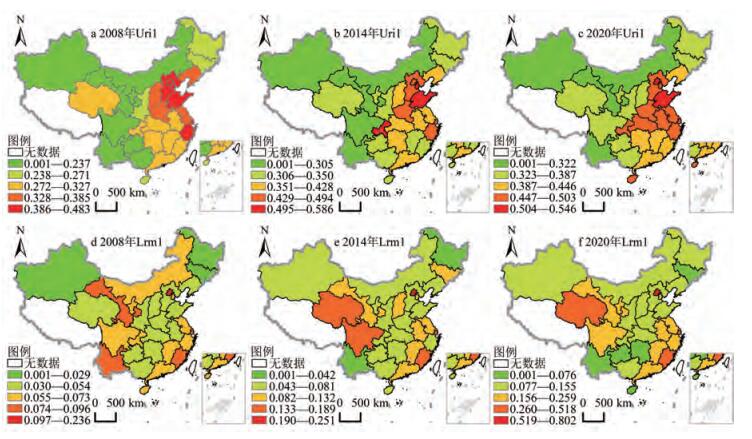
基于2008—2020年中国省级面板数据,采用熵值TOPSIS法测度城乡融合发展水平,使用双向固定效应模型和空间杜宾模型,实证检验了土地资源错配对城乡融合发展的影响。研究发现:①土地资源错配抑制了城乡融合发展;从各维度看,土地资源错配对城乡经济、社会和空间信息融合具有显著的抑制作用,但对城乡人口融合、生态融合影响不显著。②“双循环”新发展格局在土地资源错配抑制城乡融合发展过程中发挥着负向调节作用,能够缓解土地资源错配对城乡融合发展的不利影响。③土地资源错配对城乡融合发展的影响具有显著的空间溢出效应,阻碍了邻近地区的城乡融合发展。因此,应优化土地资源的供给结构,提高土地资源配置效率;同时提升贸易开放水平,激活内需发展活力;加强土地资源配置的区域联动性,推动城乡融合发展。
Based on China's provincial panel data from 2008 to 2020, the entropy value TOPSIS method is used to measure the level of urban-rural integration and development, and the impact of land resource mismatch on urban-rural integration and development is empirically examined using the two-way fixed-effects model and the spatial Durbin model. The study finds that: 1) land resource mismatch inhibits urban-rural integration development; from the perspective of various dimensions, land resource mismatch has a significant impediment to urban-rural economic, social and spatial information integration, but does not have a significant effect on urban-rural population integration and ecological integration. 2) The new development pattern of 'double-cycle' plays a negative regulatory role in the process of inhibiting urban-rural integrated development by land resource mismatch, and can alleviate the negative impact of land resource mismatch on urbanrural integrated development. 3) The impact of land resource mismatch on urban-rural integrated development has a significant spatial spillover effect, hindering urban-rural integrated development in neighboring regions. Therefore, the supply structure of land resources should be optimized to improve the efficiency of land resource allocation; at the same time, the level of trade openness should be raised to activate the vitality of the development of domestic demand; and the regional linkage of land resource allocation should be strengthened to promote urban-rural integrated development.
城乡融合发展 / 土地资源错配 / 贸易开放水平 / 内需依赖度
integrated urban-rural development / misallocation of land resources / level of trade openness / domestic demand dependence
| 1 |
叶璐, 王济民. 我国城乡差距的多维测定[J]. 农业经济问题, 2021 (2): 123- 134.
|
| 2 |
陈坤秋, 龙花楼. 中国土地市场对城乡融合发展的影响[J]. 自然资源学报, 2019, 34 (2): 221- 235.
|
| 3 |
|
| 4 |
陈恭军. 土地资源错配、产业结构与雾霾污染——基于空间计量和动态面板门槛模型的实证分析[J]. 中国软科学, 2022 (12): 143- 152.
|
| 5 |
钱文荣. 中国城市土地资源配置中的市场失灵、政府缺陷与用地规模过度扩张[J]. 经济地理, 2001 (4): 456- 460.
|
| 6 |
丁志国, 赵宣凯, 苏治. 中国经济增长的核心动力——基于资源配置效率的产业升级方向与路径选择[J]. 中国工业经济, 2012 (9): 18- 30.
|
| 7 |
|
| 8 |
|
| 9 |
|
| 10 |
|
| 11 |
赖敏. 土地要素错配阻碍了中国产业结构升级吗?——基于中国230个地级市的经验证据[J]. 产业经济研究, 2019 (2): 39- 49.
|
| 12 |
安勇, 赵丽霞. 土地资源错配、空间策略互动与城市创新能力[J]. 中国土地科学, 2021, 35 (4): 17- 25.
|
| 13 |
毛文峰, 陆军. 土地要素错配如何影响中国的城市创新创业质量——来自地级市城市层面的经验证据[J]. 产业经济研究, 2020 (3): 17- 29.
|
| 14 |
谢冬水. 土地供给干预与城乡收入差距——基于中国105个城市的面板数据[J]. 经济科学, 2018 (3): 35- 48.
|
| 15 |
谢冬水. 土地资源错配与城市创新能力——基于中国城市面板数据的经验研究[J]. 经济学报, 2020, 7 (2): 86- 112.
|
| 16 |
|
| 17 |
余运江, 高向东. 市场潜能、住房价格与劳动力流动——基于新经济地理学的视角[J]. 产业经济研究, 2017 (6): 117- 126.
|
| 18 |
李勇刚, 罗海艳. 土地资源错配阻碍了产业结构升级吗?——来自中国35个大中城市的经验证据[J]. 财经研究, 2017, 43 (9): 110- 121.
|
| 19 |
张少辉, 余泳泽. 土地出让、资源错配与全要素生产率[J]. 财经研究, 2019, 45 (2): 73- 85.
|
| 20 |
张雄, 张安录, 邓超. 土地资源错配及经济效率损失研究[J]. 中国人口·资源与环境, 2017, 27 (3): 170- 176.
|
| 21 |
陆铭, 张航, 梁文泉. 偏向中西部的土地供应如何推升了东部的工资[J]. 中国社会科学, 2015 (5): 59- 83.
|
| 22 |
张苗, 彭山桂, 刘璇. 土地资源错配阻碍新旧动能转换的作用机制研究[J]. 中国土地科学, 2020, 34 (11): 95- 102.
|
| 23 |
|
| 24 |
齐心, 陈珏颖, 刘合光. 以新发展理念推进城乡融合发展: 逻辑与路径[J]. 经济社会体制比较, 2023 (2): 14- 23.
|
| 25 |
刘同山, 高跃婷. 基于新发展理念构建城乡融合发展新格局: 重点问题与关键举措[J]. 华中农业大学学报(社会科学版), 2024 (6): 37- 50.
|
| 26 |
李锴, 齐绍洲. 贸易开放、经济增长与中国二氧化碳排放[J]. 经济研究, 2011, 46 (11): 60- 72.
|
| 27 |
陈思宇, 陈斌开. 贸易、就业与中国农村贫困[J]. 改革, 2020 (9): 80- 93.
|
| 28 |
魏浩, 赵春明. 对外贸易对我国城乡收入差距影响的实证分析[J]. 财贸经济, 2012 (1): 78- 86.
|
| 29 |
李勇刚, 王猛. 土地财政与产业结构服务化——一个解释产业结构服务化"中国悖论"的新视角[J]. 财经研究, 2015, 41 (9): 29- 41.
|
| 30 |
周佳宁, 秦富仓, 刘佳, 等. 多维视域下中国城乡融合水平测度、时空演变与影响机制[J]. 中国人口·资源与环境, 2019, 29 (9): 166- 176.
|
| 31 |
李力行, 黄佩媛, 马光荣. 土地资源错配与中国工业企业生产率差异[J]. 管理世界, 2016 (8): 86- 96.
|
| 32 |
杨其静, 卓品, 杨继东. 工业用地出让与引资质量底线竞争——基于2007—2011年中国地级市面板数据的经验研究[J]. 管理世界, 2014 (11): 24- 34.
|
| 33 |
周德, 戚佳玲, 钟文钰. 城乡融合评价研究综述: 内涵辨识、理论认知与体系重构[J]. 自然资源学报, 2021, 36 (10): 2634- 2651.
|
| 34 |
徐藜丹, 邓祥征, 姜群鸥, 等. 中国县域多维贫困与相对贫困识别及扶贫路径研究[J]. 地理学报, 2021, 76 (6): 1455- 1470.
|
| 35 |
|
| 36 |
|
| 37 |
胡深, 吕冰洋. 经济增长目标与土地出让[J]. 财政研究, 2019 (7): 46- 59.
|
| 38 |
吴敏, 周黎安. 晋升激励与城市建设: 公共品可视性的视角[J]. 经济研究, 2018, 53 (12): 97- 111.
|
| 39 |
邵帅, 范美婷, 杨莉莉. 经济结构调整、绿色技术进步与中国低碳转型发展——基于总体技术前沿和空间溢出效应视角的经验考察[J]. 管理世界, 2022, 38 (2): 46- 69.
|
| 40 |
王贤彬, 张莉, 徐现祥. 地方政府土地出让、基础设施投资与地方经济增长[J]. 中国工业经济, 2014 (7): 31- 43.
|
| 41 |
文东伟, 冼国明. 中国制造业的空间集聚与出口: 基于企业层面的研究[J]. 管理世界, 2014 (10): 57- 74.
|
/
| 〈 |
|
〉 |