 PDF(1790 KB)
PDF(1790 KB)


城市群多中心性对城乡融合发展的影响——以中国十大城市群为例
崔家兴, 彭雅雯, 孔雪松, 孙建伟, 靳涵, 郑文升
人文地理 ›› 2025, Vol. 40 ›› Issue (5) : 133-144.
 PDF(1790 KB)
PDF(1790 KB)
 PDF(1790 KB)
PDF(1790 KB)
城市群多中心性对城乡融合发展的影响——以中国十大城市群为例
THE INFLUENCE OF URBAN AGGLOMERATION POLYCENTRICITY ON URBAN-RURAL INTEGRATION DEVELOPMENT: A CASE STUDY OF CHINA'S TEN URBAN AGGLOMERATIONS
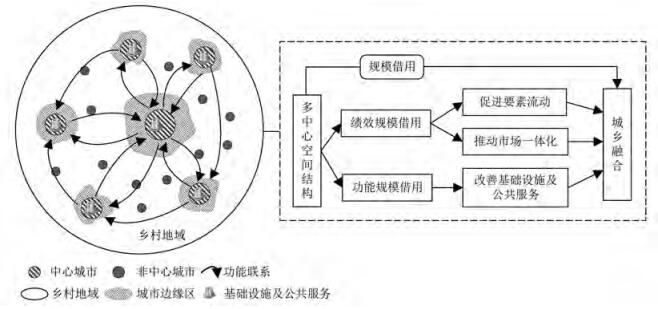
探究城市群多中心性对城乡融合发展的影响,对优化城市群空间结构和全面推进城乡融合发展至关重要。以十大城市群为研究对象,考察其多中心性对城乡融合发展的影响。结果表明:①长三角、珠三角、成渝、山东半岛和粤闽浙城市群大致呈现向多中心发展的态势,而其余城市群呈多中心性减弱趋势。②各城市群的城乡融合水平整体呈稳步上升态势。保持前列的是京津冀、长三角和珠三角城市群。各城市群的城乡融合水平在空间上存在显著差异,中高度及高度融合区环绕中度融合区分布。③城市群多中心性与城乡融合发展呈显著的先上升后下降的倒U型变化趋势。④处于不同发展阶段的城市群,其多中心性对城乡融合的影响存在差异。
Based on the data of 162 prefecture-level cities of ten urban agglomerations from 2012 to 2021, this study examines the impact of urban agglomeration polycentricity on urban-rural integration. The results show that: 1)The Yangtze River Delta, the Pearl River Delta, Chengdu-Chongqing, Shandong Peninsula and Guangdong, Fujian and Zhejiang urban agglomerations generally show a trend toward polycentricity, while other urban agglomerations show a tendency of weakening polycentricity. 2)The overall level of urban-rural integration of ten urban agglomerations shows a steady increase. There are significant spatial differences in the level of urban-rural integration among ten urban agglomerations, with medium-high and high integration zones distributed around medium integration zones. 3) The polycentricity of urban agglomerations and urbanrural integration show a significant inverted U-shaped relationship. 4)The influence of polycentricity on urban-rural integration varies among urban agglomerations at different stages of development.
urban agglomerations / polycentricity / urban-rural integration / spatial structure
| 1 |
胡国建, 陈传明, 金星星, 等. 中国城市体系网络化研究[J]. 地理学报, 2019, 74 (4): 681- 693.
|
| 2 |
刘生龙, 胡鞍钢. 交通基础设施与经济增长: 中国区域差距的视角[J]. 中国工业经济, 2010 (4): 14- 23.
|
| 3 |
方创琳, 王振波, 马海涛. 中国城市群形成发育规律的理论认知与地理学贡献[J]. 地理学报, 2018, 73 (4): 651- 665.
|
| 4 |
孙斌栋, 王旭辉, 蔡寅寅. 特大城市多中心空间结构的经济绩效——中国实证研究[J]. 城市规划, 2015, 39 (8): 39- 45.
|
| 5 |
陈玉, 孙斌栋. 京津冀存在"集聚阴影"吗——大城市的区域经济影响[J]. 地理研究, 2017, 36 (10): 1936- 1946.
|
| 6 |
刘维奇, 吴明月, 张金龙. 多中心空间结构对城乡融合发展的影响研究[J]. 管理学刊, 2024, 37 (1): 24- 41.
|
| 7 |
魏晓彤, 冯鲍, 阎世平. 数字经济对城乡融合发展的影响及其作用机制[J]. 技术经济与管理研究, 2024 (1): 153- 158.
|
| 8 |
戈大专, 孙攀, 汤礼莎, 等. 国土空间规划支撑城乡融合发展的逻辑与路径[J]. 中国土地科学, 2023, 37 (1): 1- 9.
|
| 9 |
刘修岩, 李松林, 陈子扬. 多中心空间发展模式与地区收入差距[J]. 中国工业经济, 2017 (10): 25- 43.
|
| 10 |
王妤, 孙斌栋. 城市规模分布对地区收入差距的影响——基于LandScan全球人口数据库的实证研究[J]. 城市发展研究, 2021, 28 (6): 25- 32.
|
| 11 |
曾鹏, 李洪涛, 邢小玉, 等. 中心城市首位度对区域经济协调发展的影响研究——基于中国19个城市群的分析[J]. 重庆大学学报(社会科学版), 2023, 29 (1): 56- 69.
|
| 12 |
王彩艳, 刘修岩. 城市群多中心空间结构对乡村振兴的影响——基于中国19个城市群的实证分析[J]. 经济地理, 2023, 43 (1): 55- 63.
|
| 13 |
杨桐彬, 朱英明, 杜家禛. 中国城市群是否存在借用规模?[J]. 地理科学进展, 2022, 41 (7): 1156- 1167.
|
| 14 |
姚常成, 宋冬林. 借用规模、网络外部性与城市群集聚经济[J]. 产业经济研究, 2019 (2): 76- 87.
|
| 15 |
|
| 16 |
|
| 17 |
|
| 18 |
石敏俊, 张瑜, 郑丹. 城市群空间结构对地区间收入差距的影响研究[J]. 经济纵横, 2023 (2): 90- 101.
|
| 19 |
|
| 20 |
|
| 21 |
宋林, 张蕾蕾. 城市群多中心空间结构与地区收入差距——基于我国十大城市群的实证分析[J]. 经济问题探索, 2023 (4): 86- 101.
|
| 22 |
程刚, 赵长娟. 多中心空间发展模式是否有助于缩小城乡收入差距?[J]. 财贸研究, 2023, 34 (3): 15-27, 67.
|
| 23 |
孙婧芳. 城市劳动力市场中户籍歧视的变化: 农民工的就业与工资[J]. 经济研究, 2017, 52 (8): 171- 186.
|
| 24 |
陈姝兴, 丁登龙, 吴康. 借用规模视角下中国城市收缩时空特征及其空间溢出效应[J]. 经济地理, 2024, 44 (3): 66- 75.
|
| 25 |
孙东琪, 鲁嘉颐, 张明斗, 等. 借用规模与集聚阴影视角下中国小城镇服务功能评估——以苏南地区为例[J]. 地理科学进展, 2022, 41 (2): 199- 213.
|
| 26 |
程开明. 聚集抑或扩散——城市规模影响城乡收入差距的理论机制及实证分析[J]. 经济理论与经济管理, 2011 (8): 14- 23.
|
| 27 |
|
| 28 |
张玎. 基于Zipf法则的浙江省城市规模分析[J]. 对外经贸, 2011 (12): 96- 98.
|
| 29 |
|
| 30 |
周佳宁, 秦富仓, 刘佳, 等. 多维视域下中国城乡融合水平测度、时空演变与影响机制[J]. 中国人口·资源与环境, 2019, 29 (9): 166- 176.
|
| 31 |
徐姗, 吴青青. 中国城乡融合水平时空分异特征及影响因素分析[J]. 统计与决策, 2023, 39 (20): 114- 119.
|
| 32 |
王富喜, 毛爱华, 李赫龙, 等. 基于熵值法的山东省城镇化质量测度及空间差异分析[J]. 地理科学, 2013, 33 (11): 1323- 1329.
|
| 33 |
|
| 34 |
陈坤秋, 龙花楼. 中国土地市场对城乡融合发展的影响[J]. 自然资源学报, 2019, 34 (2): 221- 235.
|
| 35 |
胡永浩, 胡南燕, 杨嘉乐, 等. 数字乡村建设对城乡融合发展的影响及其机制研究——基于要素双向流动视角[J]. 经济问题探索, 2024 (10): 45- 59.
|
| 36 |
廖祖君, 王理, 杨伟. 经济集聚与区域城乡融合发展——基于空间计量模型的实证分析[J]. 软科学, 2019, 33 (8): 54-60, 72.
|
| 37 |
周佳宁, 邹伟, 秦富仓, 等. 值化理念下中国城乡融合多维审视及影响因素[J]. 地理研究, 2020, 39 (8): 1836- 1851.
|
| 38 |
周心怡, 李南, 龚锋. 新型城镇化、公共服务受益均等与城乡收入差距[J]. 经济评论, 2021 (2): 61- 82.
|
| 39 |
|
| 40 |
陆军, 毛文峰. 城市网络外部性的崛起: 区域经济高质量一体化发展的新机制[J]. 经济学家, 2020 (12): 62- 70.
|
/
| 〈 |
|
〉 |